Disaster recovery is a critical component of any robust IT strategy, especially in the cloud. AWS offers a variety of services that can be harnessed to create effective and resilient disaster recovery (DR) plans. In this blog post, we will explore how to leverage AWS services like S3 and Glacier for disaster recovery solutions.
AWS S3 and Glacier
Amazon S3 and Glacier are two powerful AWS storage services. S3 provides high-availability storage, ideal for keeping backups readily accessible, while Glacier is cost-effective for long-term archival. Both are integral to a layered DR strategy.
AWS DR Principles
- Data Backup and Storage
- Utilise Amazon S3 for regular backups of critical data.
- For cost-effective long-term storage, transition older backups to Amazon Glacier.
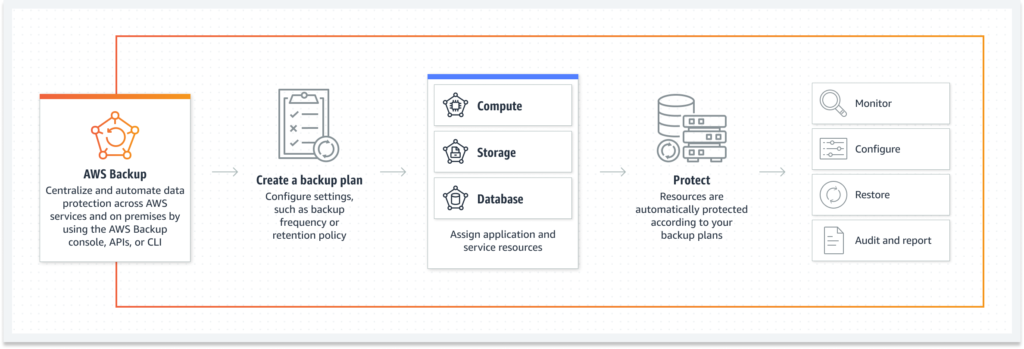
- Automated Backup Solutions
- Implement AWS Backup, a fully managed service to automate backup across AWS services.
- Schedule regular backups and define retention policies.
- Cross-Region Replication for S3
- Use S3’s cross-region replication feature to duplicate data across multiple AWS regions, ensuring availability in case of regional disruptions.
- Snapshot and AMI Management
- Regularly create snapshots of EC2 instances and volumes.
- Use Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) for quick restoration.
- Database Backup Strategies
- Leverage Amazon RDS to automate database backups.
- Employ point-in-time recovery features for databases like Amazon Aurora.
Implementing a DR Plan on AWS
- Assessment and Planning
- Begin with a risk assessment and identify critical workloads.
- Develop a DR plan that specifies recovery objectives, tools, and processes.
- Implementation of Backup Strategies
- Set up S3 and Glacier for storing backups.
- Implement cross-region replication and automate backup processes.
- Regular Testing and Evaluation
- Regularly test the recovery processes to ensure they meet the business’s Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO).
- Adjust the DR strategy based on test outcomes and evolving business needs.
- Integration with CloudFormation:
- Use AWS CloudFormation to script and automate the deployment of infrastructure, ensuring quick restoration of services in a disaster scenario.
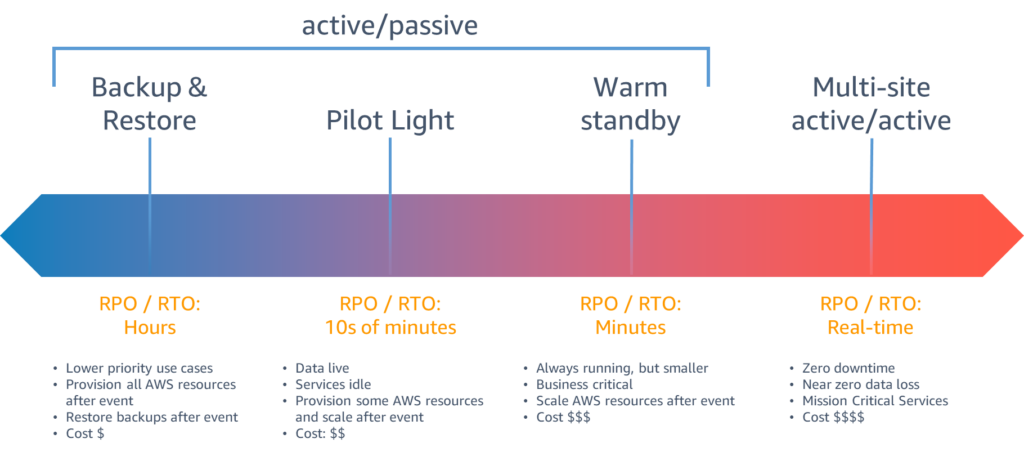
The image below shows the scale and impact of different disaster recovery scenarios, each depending on the customers appetite for cloud spend vs minimising RPO and RTO times.
Conclusion
A well-implemented disaster recovery plan on AWS leverages the robust and scalable infrastructure of the cloud. By using services like Amazon S3, Glacier, AWS Backup, and RDS, businesses can ensure that their critical data and applications are protected against unforeseen disasters, minimizing downtime and data loss.



